What Is Inside a Tubular Motor?
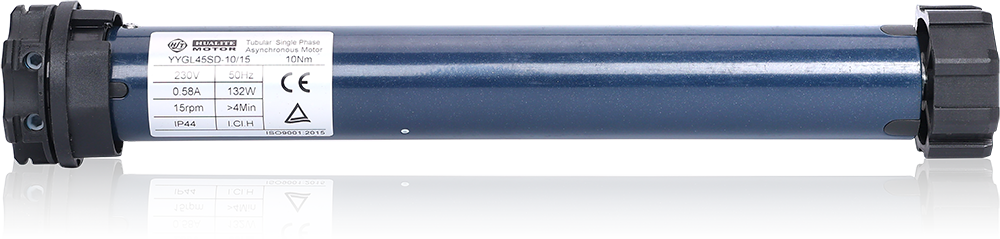
A tubular motor may look simple from the outside, but inside it contains a carefully engineered system of mechanical and electrical components. Each part plays a crucial role in delivering smooth, reliable, and long-lasting operation for roller blinds, shutters, awnings, and screens. Understanding what is inside a tubular motor helps buyers evaluate quality, performance, and durability.
1. Electric Motor (Stator and Rotor)
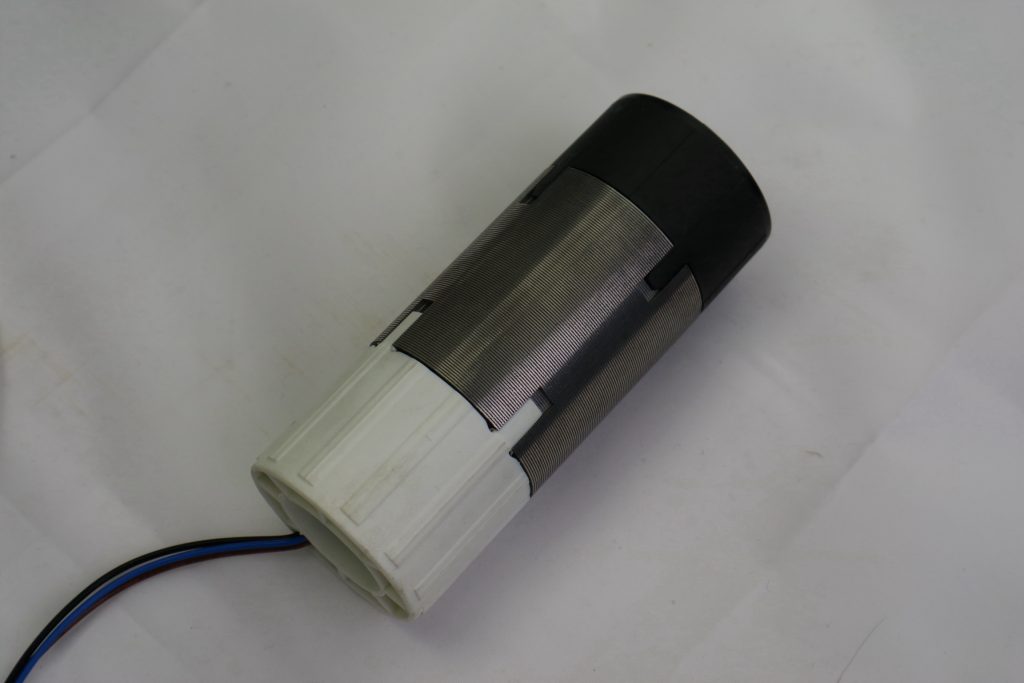

At the core of every tubular motor is the electric motor itself, consisting of two main parts:
- Stator: Made of laminated silicon steel sheets with copper windings. The quality of the copper wire and winding process directly affects efficiency, torque stability, and heat resistance.
- Rotor: Usually made of steel with an aluminum or copper cage structure. Precision machining of the rotor ensures low vibration and quiet operation.
High-quality motors use optimized magnetic designs to reduce energy loss and improve efficiency.
2. Gearbox (Reduction System)
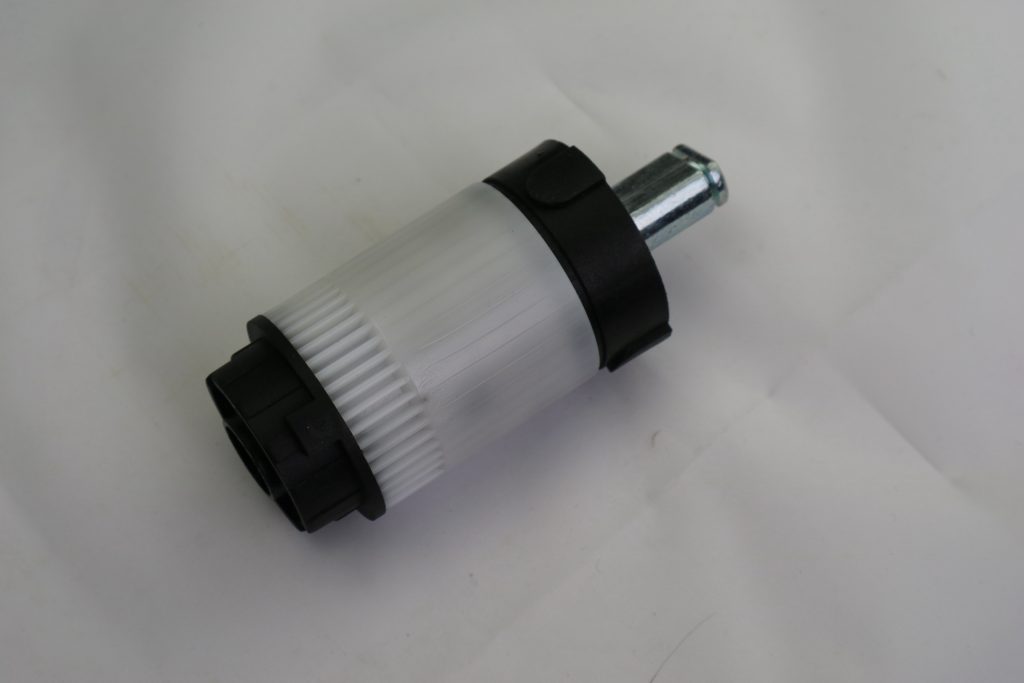

The electric motor rotates at a high speed, which is not suitable for directly driving blinds or shutters. This is where the gearbox comes in.
- The gearbox reduces speed and increases torque.
- It is typically composed of steel or reinforced metal gears.
- Precision gear alignment ensures smooth movement and long service life.
A well-designed gearbox minimizes noise and prevents gear wear under continuous load.
3. Limit Switch System
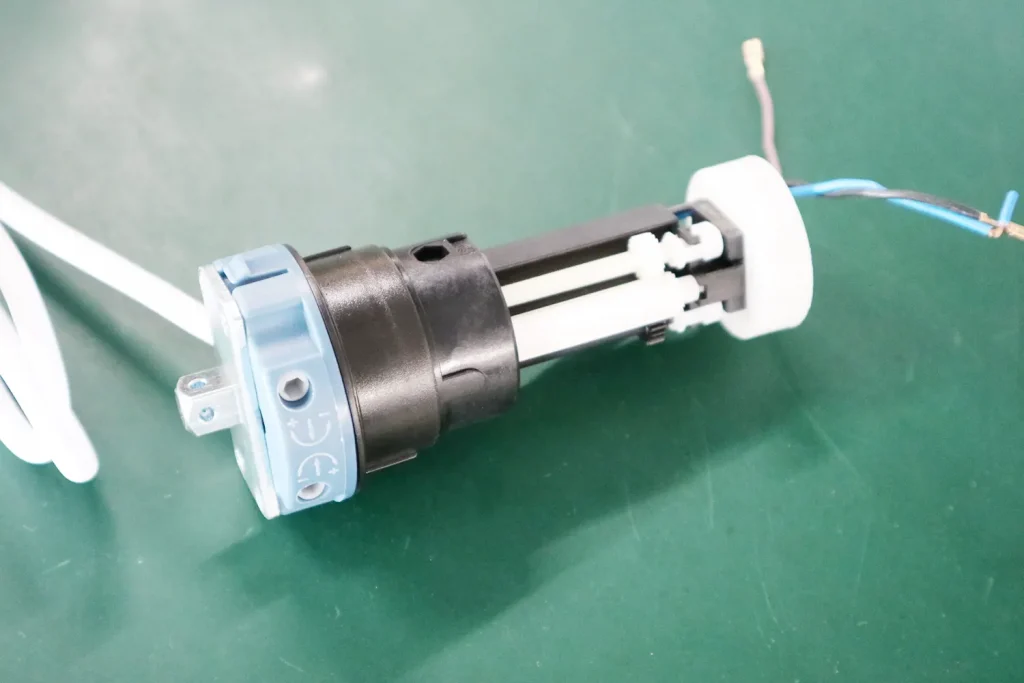

The limit switch controls how far the motor runs in each direction.
- Mechanical limit switches use adjustable cams and springs.
- Electronic limit switches rely on sensors and control boards for higher accuracy.
This system prevents over-rotation, protecting both the motor and the application. Accurate limit setting is essential for safety and consistent positioning.
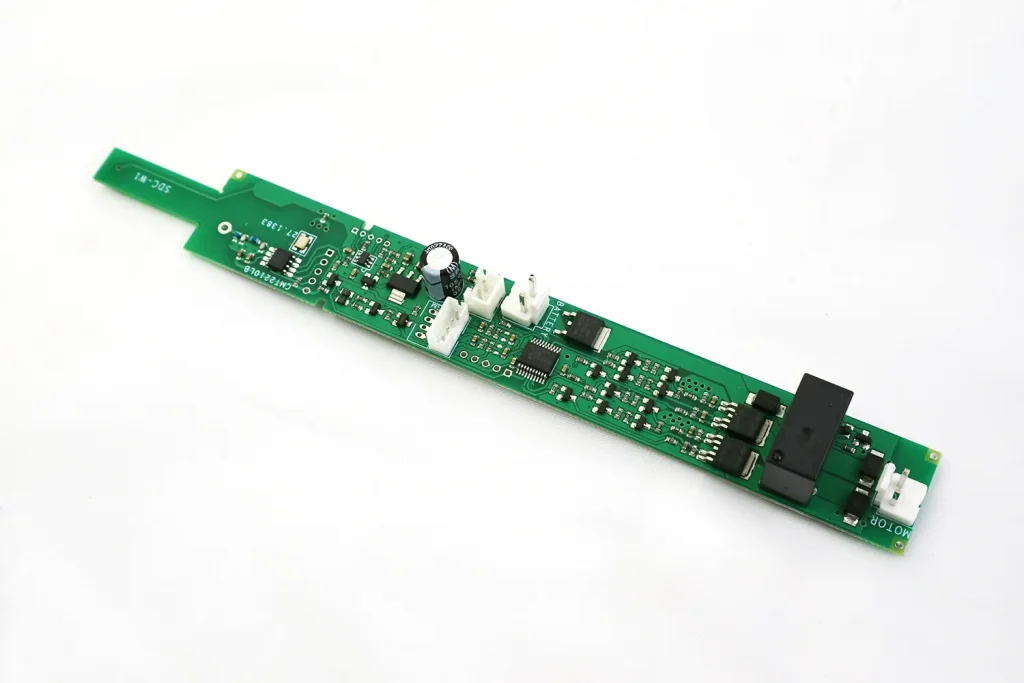
4. Brake System
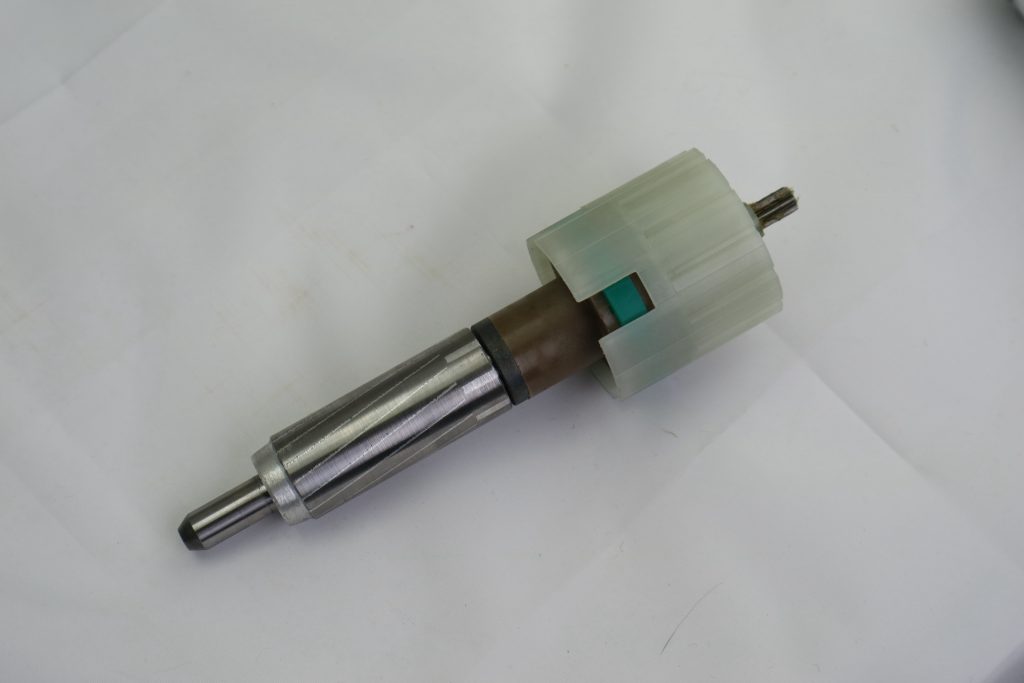

Inside the tubular motor, a brake mechanism holds the curtain, shutter, or blind in position when the motor stops.
- Usually a mechanical or electromagnetic brake
- Prevents unwanted movement caused by gravity or wind load
- Ensures precise stopping at the desired position
A reliable brake system is especially important for roller shutters and large blinds.
5. Output Shaft and Drive Components
The output shaft transfers power from the motor to the roller tube.
- Made from hardened steel for strength
- Works together with the crown and drive wheel
- Must match the tube size precisely to avoid slipping or vibration
Good alignment between the shaft and tube improves efficiency and reduces noise.
6. Bearings and Bushings
Bearings support rotating components and reduce friction.
- High-quality bearings ensure smooth rotation
- Reduce wear on the motor and gearbox
- Help maintain quiet operation over time
Inferior bearings are a common cause of early motor failure.
7. Control Electronics (Optional)

In modern tubular motors, especially smart versions, internal control electronics may include:
- Receiver modules (RF, WiFi, Zigbee)
- Control boards
- Overload and thermal protection circuits
These components enable remote control, automation, and integration with smart home systems.
8. Motor Housing and Insulation
All internal components are protected by a metal tubular housing.
- Provides structural strength
- Helps dissipate heat
- Protects against dust and minor moisture
Internal insulation materials improve electrical safety and reduce noise.
Conclusion
Inside a tubular motor is a compact yet highly sophisticated system combining electrical engineering, precision mechanics, and safety control. From the motor core and gearbox to the limit switch and brake system, every component affects performance, reliability, and lifespan.
Understanding what is inside a tubular motor allows buyers and installers to make informed decisions, compare quality levels, and choose the right motor for their specific application.



