WALTER Tubular Motor Factory
Industrial Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance System
A tubular motor is a critical driving component widely used in roller shutters, blinds, awnings, and architectural shading systems. The performance, safety, and service life of the product are determined not only by design, but fundamentally by the manufacturing capability and process control of the Tubular Motor Factory.
A professional Tubular Motor Factory integrates precision metal processing, electromagnetic manufacturing, automated assembly, and strict quality validation. The following describes the complete industrial manufacturing process from raw materials to final shipment.


1. Motor Tube Manufacturing and Surface Treatment
The motor outer tube serves as both a structural and protective component. High-strength low-carbon steel tubes are selected to ensure mechanical stability and dimensional consistency.
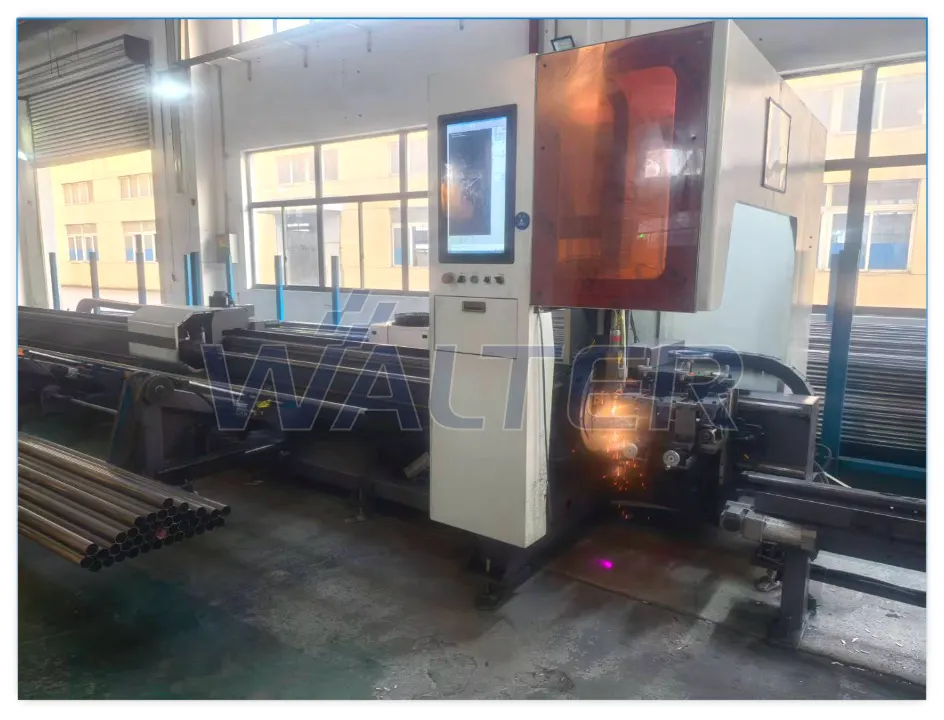


- Cold forming of motor tubes ensures accurate diameter, roundness, and concentricity
- Laser cutting provides burr-free edges and precise length control
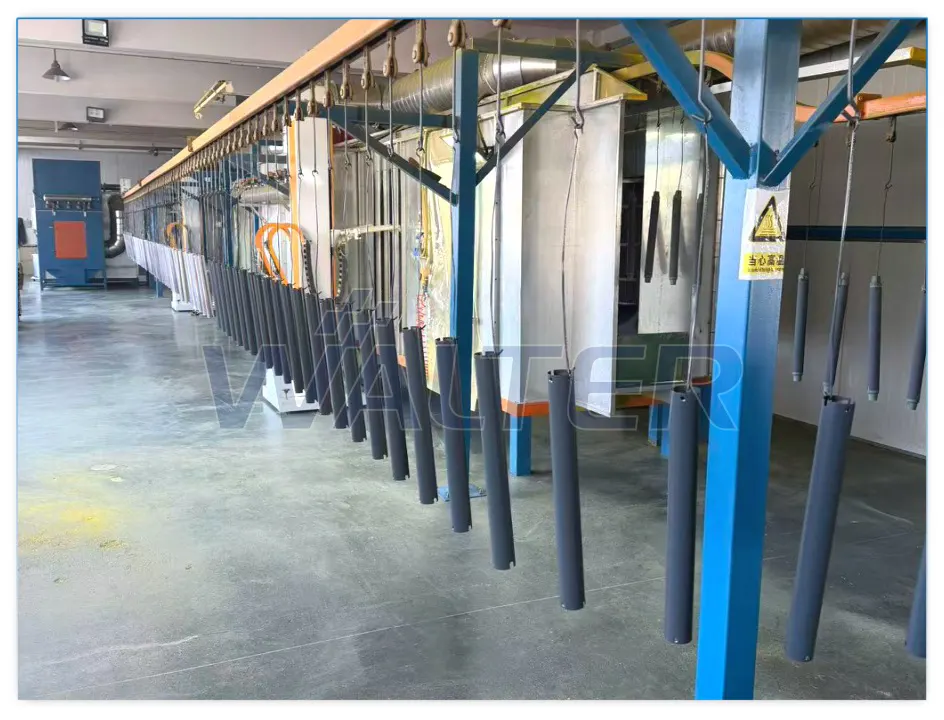
- Surface pretreatment and powder coating improve corrosion resistance, surface durability, and long-term reliability, especially for outdoor applications
2. High-Speed Stamping and Core Manufacturing
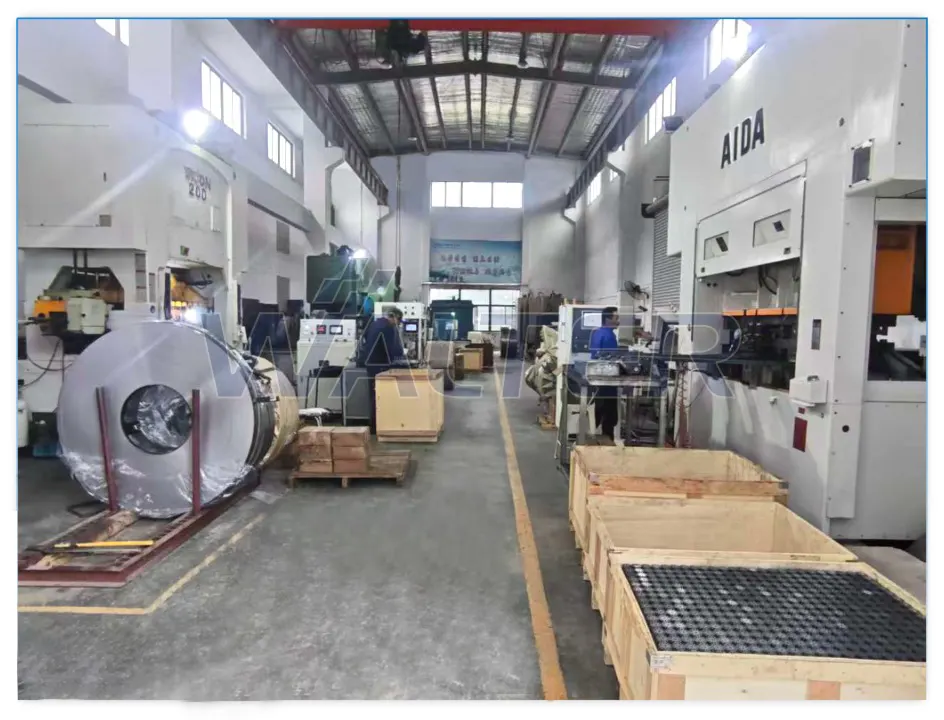
2.1 High-Speed Stamping Workshop
WALTER as a Tubular Motor Factory is equipped with 3 high-speed stamping presses, including two Yangdu presses and one Japan-made AIDA press, combining productivity with long-term precision stability.
The stamping line operates at up to 350 strokes per minute, enabling:
- High-precision stator and rotor lamination stamping
- Stable mass production with consistent tolerances
Stator and rotor laminations are processed through an automatic stacking and interlocking system, ensuring accurate alignment and secure interlocking.
After stacking, laminated cores are transferred to a CNC-controlled hydraulic press for final compaction, guaranteeing uniform core density and dimensional tolerance verification.


2.2 Stator Core Thermal Blueing Treatment
Stator cores undergo high-temperature thermal blueing treatment, which:
- Relieves internal stress generated during high-speed stamping
- Reduces magnetic iron loss
- Improves electromagnetic efficiency and thermal stability
This process is essential for producing high-efficiency, low-noise tubular motors.


3. Rotor Manufacturing and Precision Machining
3.1 Aluminum Die-Casting Rotor Process
Rotors are manufactured using high-pressure aluminum die-casting, ensuring:
- High structural density
- Excellent heat dissipation
- Stable torque transmission
Strict control of temperature and pressure minimizes porosity and internal casting defects.
3.2 Automated Shaft Press-Fitting
An automated press-fitting system inserts the rotor shaft into the die-cast rotor blank, ensuring:
- High concentricity and axial alignment
- Stable mechanical bonding
- Improved dynamic balance
3.3 Fully Automatic CNC Machining
Rotors undergo fully automatic CNC turning and precision machining, including:
- Rotor diameter finishing
- Aluminum ring machining
- Brake-side machining
- End-face finishing and critical dimensional tolerance control
This process ensures smooth operation, accurate braking performance, and long-term mechanical stability.
4. Stator Winding and Electrical Assembly
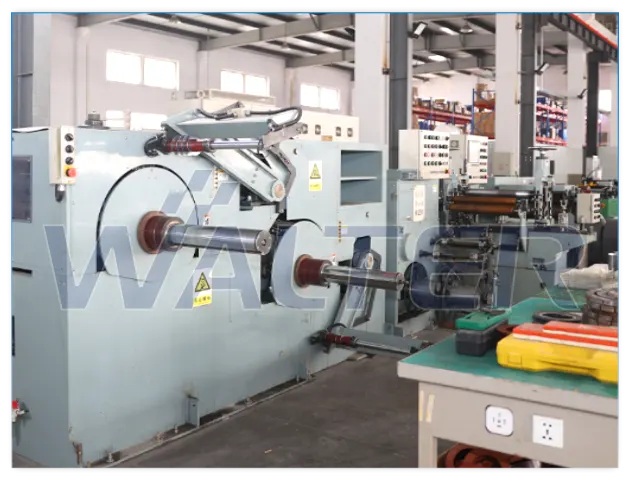
4.1 Copper Wire Winding
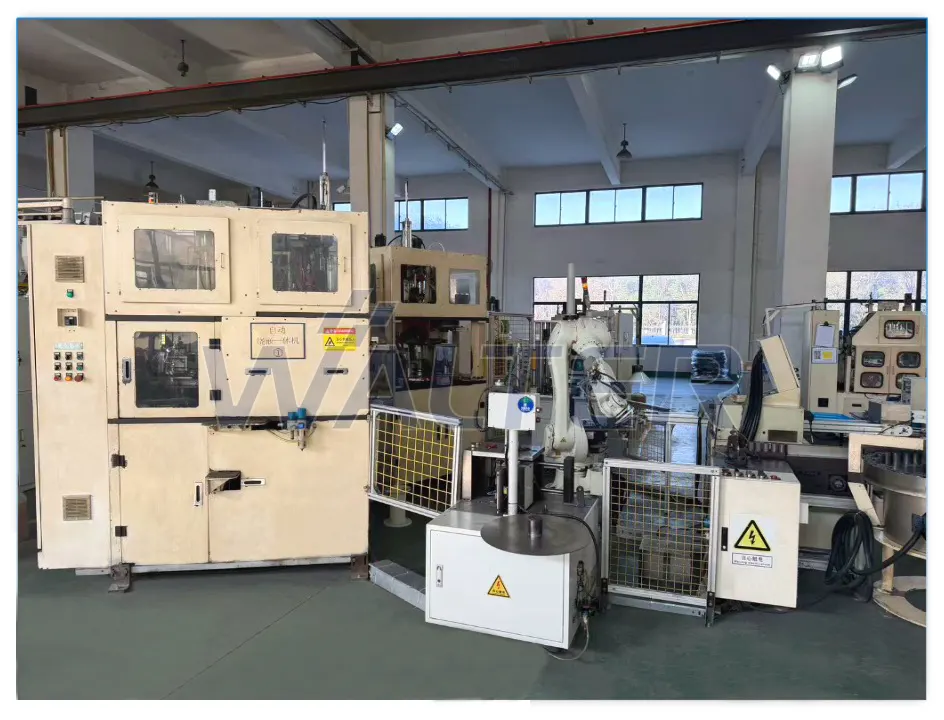


Numerical-controlled winding machines are used to ensure:
- Accurate turn count
- Controlled winding tension
- Uniform copper wire distribution
4.2 Coil Insertion and Stator Forming
Copper windings are precisely inserted into stator slots, followed by stator forming to:
- Secure coil positioning
- Improve mechanical rigidity
- Reduce electromagnetic noise
4.3 Electrical Testing of Stator Assembly
Each stator undergoes:
- High-voltage surge (Hi-Pot) testing
- Inter-turn insulation testing
All test data is recorded for quality traceability.
5. Thermal Protection and Wiring Integration
- Thermal protectors are installed to prevent overheating under overload or abnormal conditions
- Stator lead wires are connected and insulated using standardized procedures
After assembly, the stator unit is subjected to a second round of Hi-Pot and inter-turn testing to ensure electrical integrity.
6. Plastic Component Injection Molding
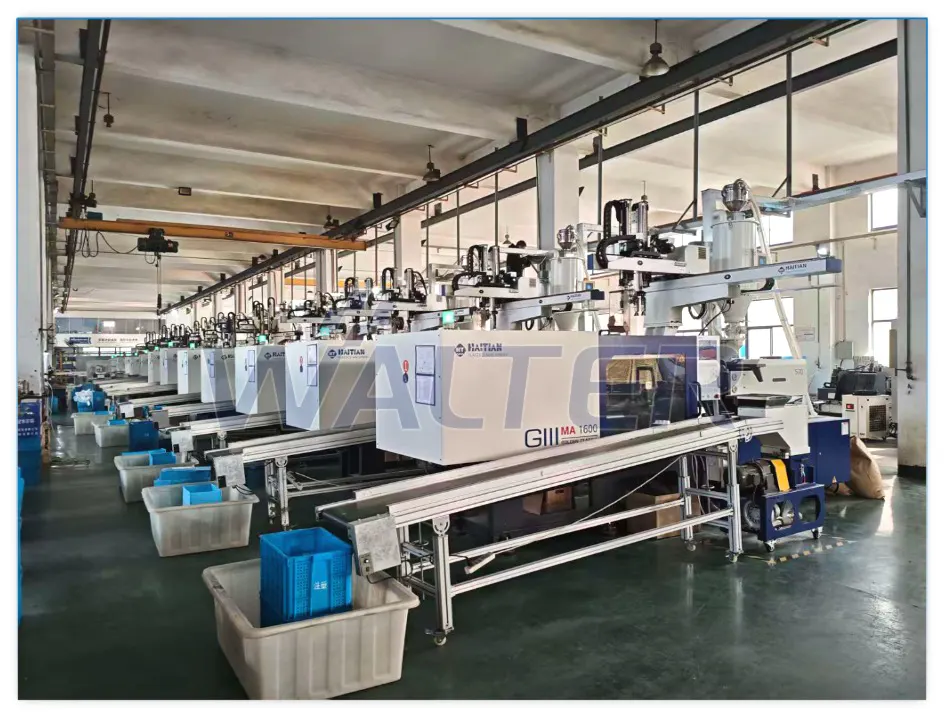

All plastic components—including motor heads, end caps, brackets, and internal structural parts—are manufactured via precision injection molding using engineering-grade plastics.
This guarantees:
- Dimensional accuracy
- Mechanical strength
- Long-term durability
7. Gear Reducer Assembly and Tubular Motor Final Assembly
7.1 Gear Reducer Assembly
The gear reducer is assembled with controlled:
- Gear meshing accuracy
- Bearing preload
- Lubrication consistency
This ensures low noise, stable torque output, and long service life.
7.2 Tubular Motor Final Assembly
Motor tube, stator, rotor, gearbox, wiring system, and protective components are integrated on standardized assembly lines using torque-controlled fastening tools and process inspection checkpoints.
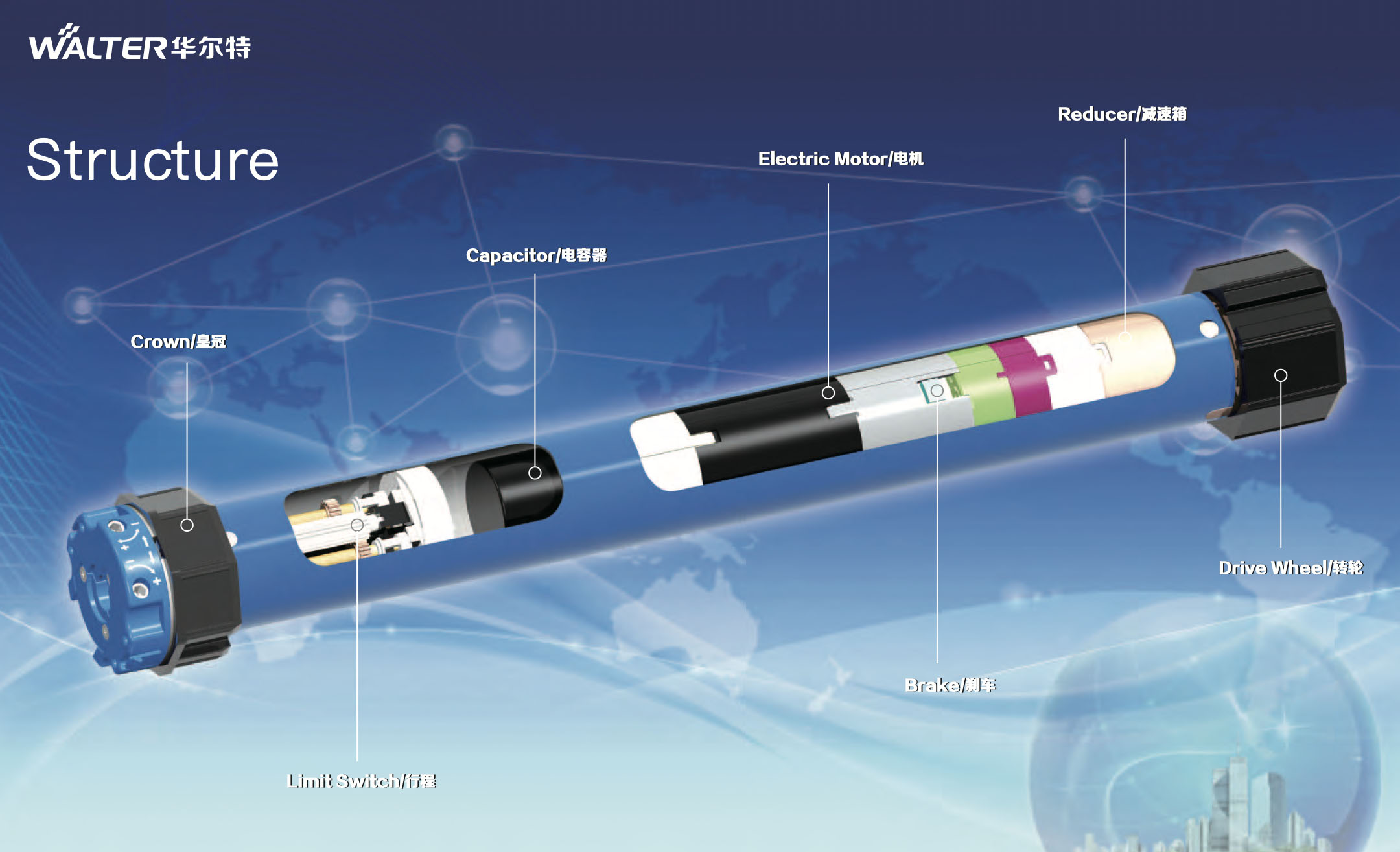

8. Comprehensive Testing and Quality Validation
8.1 Comprehensive Electrical and Functional Testing
Each assembled tubular motor undergoes comprehensive testing, including:
- Electrical Safety Testing
- Insulation resistance test
- Ground continuity (earthing resistance) test
- Dielectric withstand (Hi-Pot) test
- Abnormal Voltage Operation Testing
- High-voltage operation test
- Low-voltage operation test
- Brake Holding Force Test
Verification of braking torque to ensure safe stopping and load holding capability. - Electrical Performance Testing
- Current and power measurement under no-load conditions
- Current and power measurement under rated load conditions
- Travel Limit Adjustment and Repeatability Accuracy Test
Ensuring accurate travel setting and stable repeat positioning over multiple operating cycles.
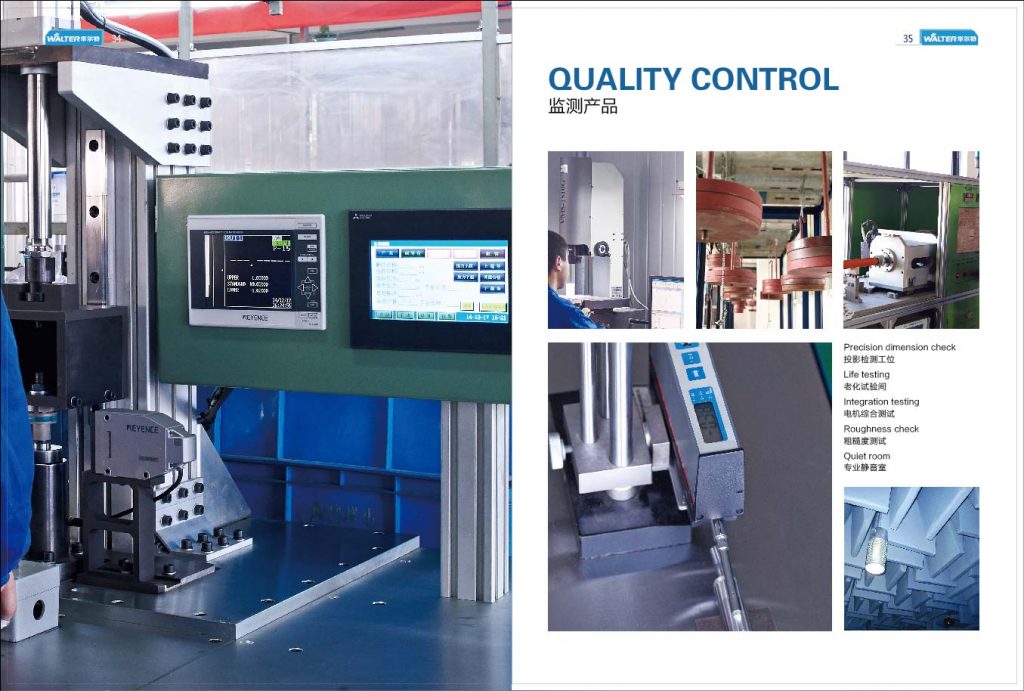
9. Aging Test, Packaging, and Shipment Control
- Sampling-based aging tests are conducted under controlled load conditions to verify thermal stability and long-term reliability
- Qualified products are packaged according to standardized procedures
- Only motors that pass all inspections are released for shipment
Each motor is traceable by production batch and inspection records, ensuring full accountability from manufacturing to delivery.

Conclusion
A professional Tubular Motor Factory is defined by systematic process control, advanced automation, and strict quality validation.
From high-speed stamping and precision machining to comprehensive electrical testing and aging verification, every manufacturing step directly contributes to the safety, reliability, and performance of tubular motors used worldwide.
This industrial-grade manufacturing approach ensures consistent quality and long-term confidence for global customers.
WALTER Tubular Motor Factory FAQs:
1. Quality Management System
Q1: Is your tubular motor factory certified to ISO standards?
A: Yes. Our tubular motor factory operates under an ISO 9001–based quality management system. All manufacturing, inspection, and traceability processes are conducted in accordance with documented ISO procedures and work instructions.
Q2: How do you control product quality throughout the production process?
A: Quality control is implemented at multiple stages, including:
- Incoming material inspection
- In-process inspection at key manufacturing steps
- Final inspection and functional testing
- Sampling-based aging and endurance testing
Each stage is documented and traceable.
2. Incoming Material Control
Q3: How are raw materials and components inspected?
A: All incoming materials, including steel tubes, copper wire, laminations, aluminum, and plastic materials, are inspected according to defined inspection standards.
Non-conforming materials are identified, segregated, and handled through corrective procedures.
Q4: Do you maintain supplier evaluation and approval records?
A: Yes. Approved suppliers are evaluated based on quality performance, delivery stability, and compliance records. Supplier performance is reviewed periodically.
3. Production Process Control
Q5: How do you ensure consistency in high-speed stamping?
A: The stamping process uses three high-speed presses (two Yangdu and one AIDA), operating at up to 350 strokes per minute.
Laminations are automatically stacked and interlocked, followed by CNC-controlled hydraulic pressing to ensure uniform core density and dimensional consistency.
Q6: How is rotor machining quality controlled?
A: Rotors undergo fully automatic CNC turning and precision machining. Critical dimensions such as rotor diameter, aluminum ring, brake-side features, and end faces are strictly controlled and verified according to defined tolerances.
Q7: How is stator winding quality ensured?
A: Stator winding is performed using numerical-controlled winding machines with controlled tension and turn count.
After winding and forming, each stator undergoes high-voltage and inter-turn insulation testing.
4. Equipment and Calibration
Q8: How do you manage production equipment maintenance?
A: All production equipment is subject to preventive maintenance plans. Maintenance records are maintained to ensure stable operation and process capability.
Q9: Are measuring and testing instruments calibrated?
A: Yes. All measuring and testing equipment are calibrated according to a defined calibration schedule. Calibration records are maintained and traceable.
5. Electrical Safety and Functional Testing
Q10: What electrical safety tests are performed on finished motors?
A: Each motor undergoes electrical safety testing, including:
- Insulation resistance test
- Ground continuity (earthing resistance) test
- Dielectric withstand (Hi-Pot) test
Q11: Do you test tubular motors under abnormal voltage conditions?
A: Yes. Motors are tested under both high-voltage and low-voltage conditions to verify stable and safe operation beyond nominal limits.
Q12: What functional performance tests are conducted?
A: Functional testing includes:
- Loading/Torque testing
- Rotation speed
- Brake holding force verification
- No-load and load current measurement
- Power consumption testing
- Travel limit adjustment and repeatability accuracy verification
6. Nonconforming Product Control
Q13: How are nonconforming products handled?
A: Nonconforming products are clearly identified, isolated, and recorded. Corrective actions are implemented based on root cause analysis before release or rework.
Q14: Do you conduct corrective and preventive actions (CAPA)?
A: Yes. CAPA procedures are implemented to address root causes of quality issues and prevent recurrence. Effectiveness is reviewed and documented.
7. Traceability and Records
Q15: Is product traceability implemented?
A: Yes. Products are traceable by production batch and inspection records, including electrical testing and aging test results.
Q16: How long are quality records retained?
A: Quality records are retained according to internal procedures and customer requirements to ensure full traceability.
8. Aging Test and Reliability
Q17: Do you perform aging or endurance testing?
A: Yes. Sampling-based aging tests are conducted under controlled load conditions to verify thermal stability, operational reliability, and performance consistency.
9. Packaging, Storage, and Shipment
Q18: How do you control packaging and shipment quality?
A: Products are packaged according to standardized procedures. Only products that pass all inspections are released for shipment.
10. Continuous Improvement
Q19: How do you ensure continuous improvement?
A: Continuous improvement is achieved through internal audits, customer feedback analysis, corrective actions, and regular management reviews.
Q20: Are employees trained for their assigned tasks?
A: Yes. All operators receive job-specific training and are qualified before independent operation. Training records are maintained.


